APPLICATIONS
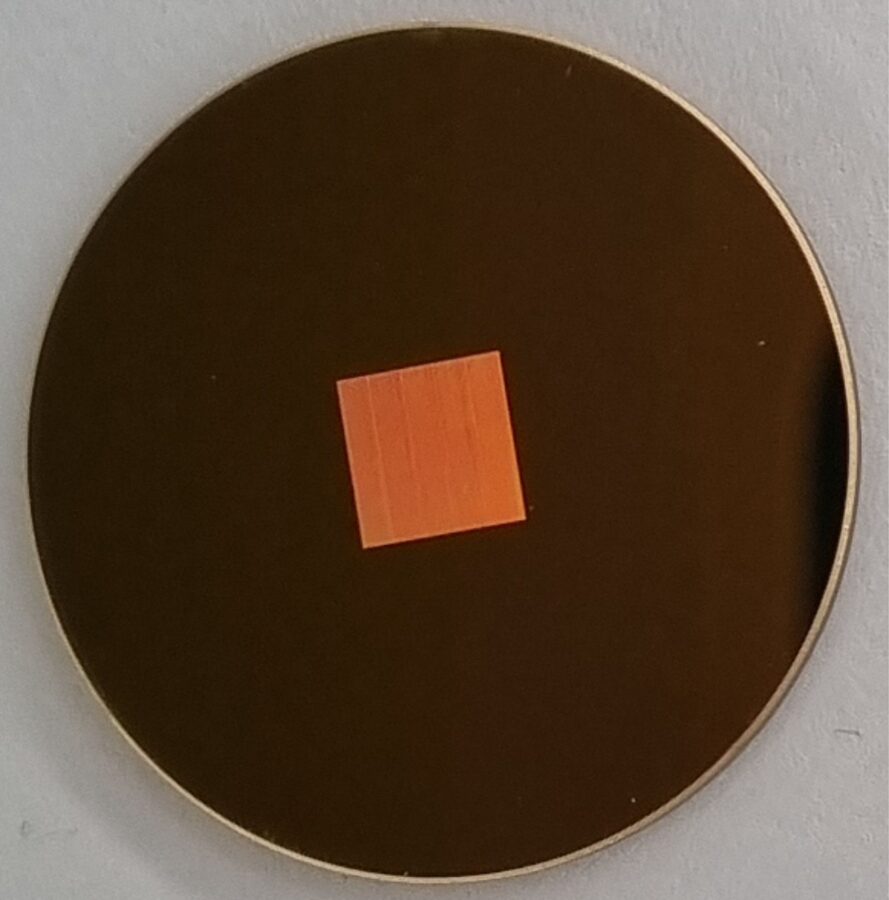
SURFACE LATTICE RESONANCES IN GOLD MICROBUMPS ARRAY
Surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) based light-matter interactions play a major role in photonic sensor applications. In order to implement such sensors in microchip devices or reduce the fabrication costs, a method with high flexibility and large-scale capabilities must be developed. Here, the formation of large-scale gold microbumps arrays by using a direct laser writing technique is presented. The fabricated arrays exhibit the surface lattice plasmon polaritons in the VIS-NIR range, in the same range as metallic gratings fabricated by lithography-based techniques. The peak of hybrid lattice plasmon resonance depends on the period of the fabricated arrays, the thickness of the gold film, coupled light polarization, and sample orientation. The demonstrated method shows relevant technological progress in the formation of large-scale metallic gratings by using a cost-effective laser-based technique. It paves new opportunities for surface lattice plasmons-based applications in biotechnology, photonics, plasmonics, etc.
Source: [ 10.1002/adom.202100027 ]
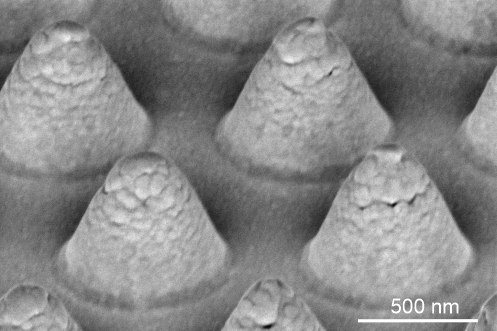
BESSEL-LIKE BEAM USE IN MICROFABRICATION
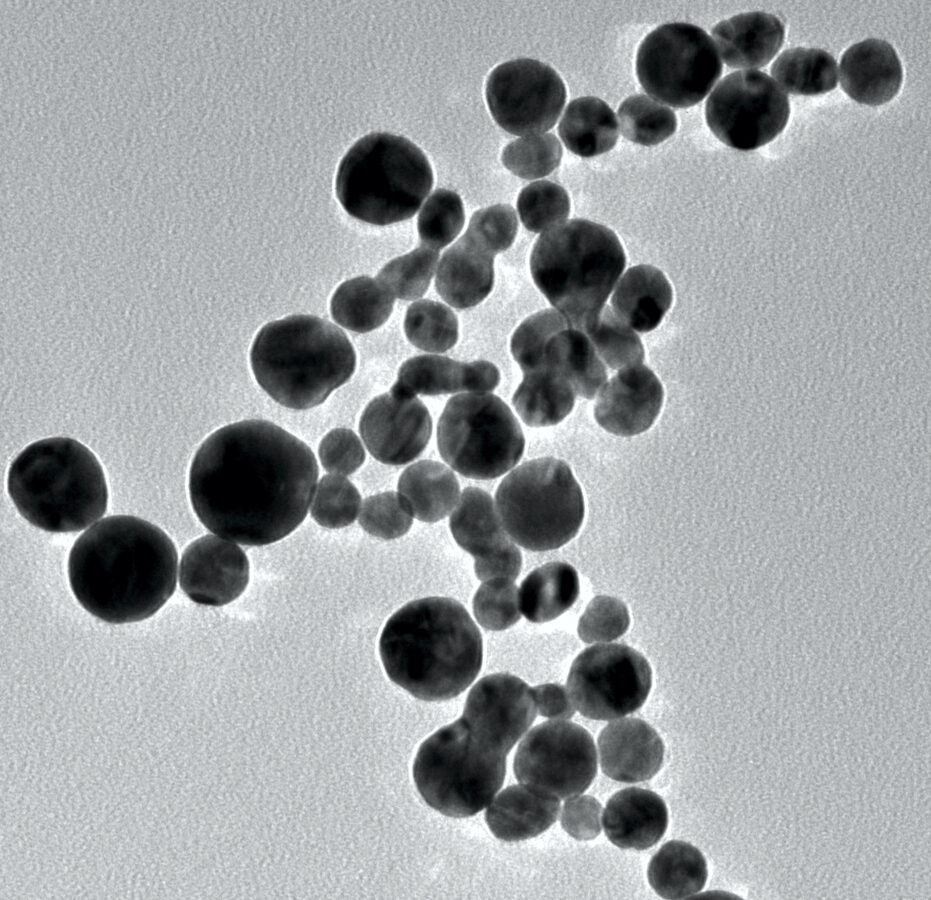
A novel laser-based method for the fabrication of concentric microrings consisting of gold micro-and nanoparticles was developed. This technique is based on the Bessel-like beam generation using polymeric microstructures which were fabricated by using laser interference lithography. The fabricated microrings structures demonstrate plasmonic characteristics. This technique provides unique possibilities for the realization of plasmonic lenses, which may find broad applications in near-field imaging, sensing, lithography, nanoparticle manipulations, etc.
Source: [ 10.1002/andp.201700174 ]
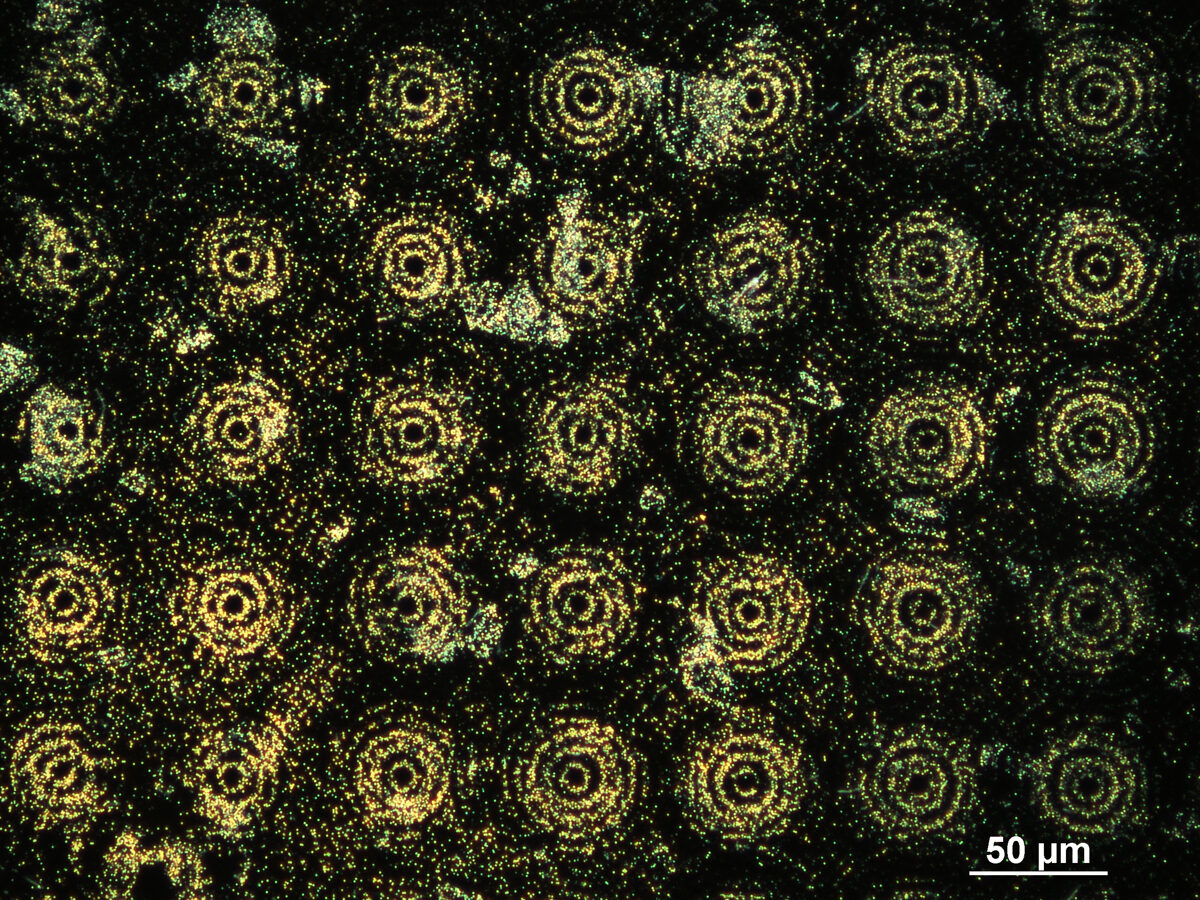
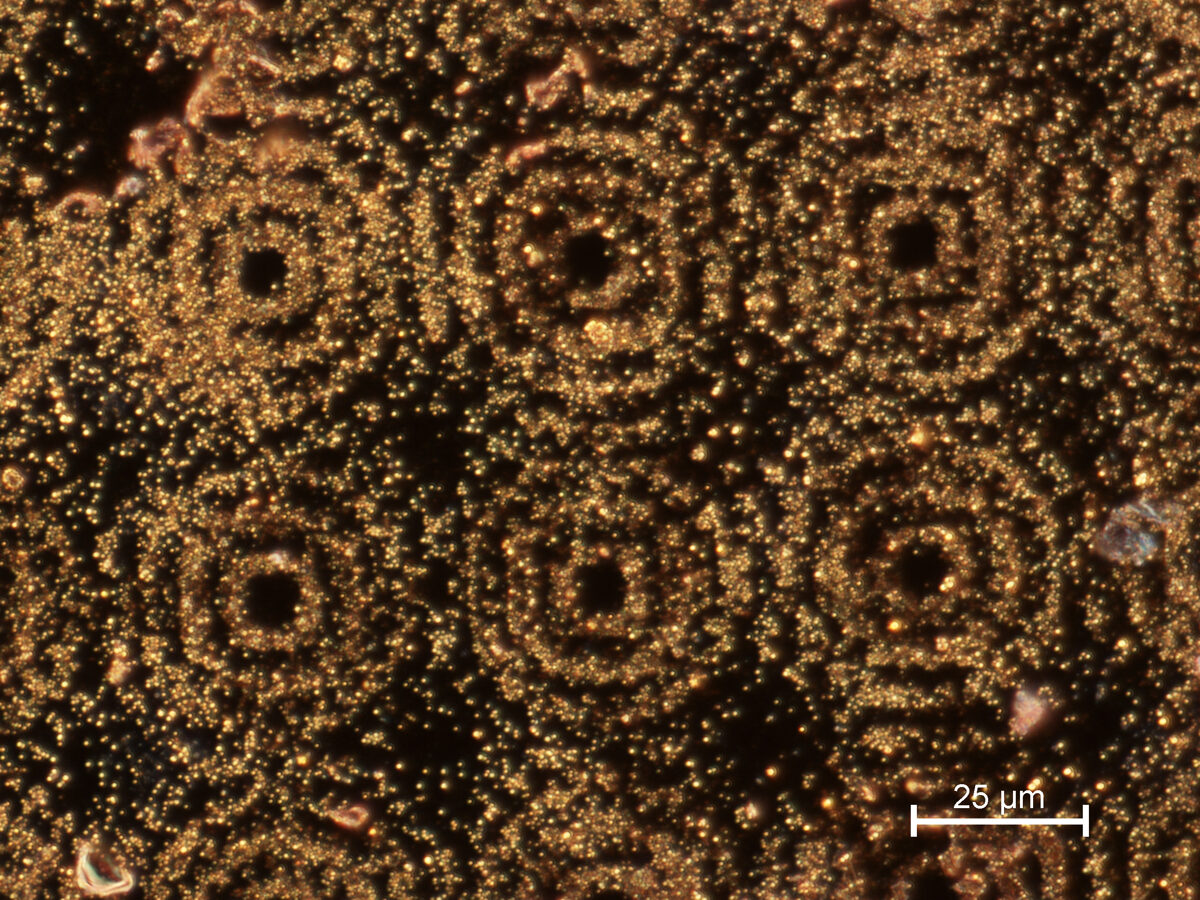
BESSEL-LIKE BEAM USE IN SERS SUBSTRATES PRODUCTION
Concentric microring structures containing gold nanoparticles were fabricated using a Bessel-like beam array with the 30 μm and 60 μm periods. The fabricated structures coated with a 5 nm thick gold layer demonstrate enhancement of Raman signals due to their induced localized plasmon resonance. The measured Raman signal intensity of self-assembled monolayers from thiols with terminal phenylalanine ring group using various Raman spectrometers exhibit that concentric gold nanoparticles structures enhance the Raman signal from different size of analyzing area. The demonstrated method provides a facile fabrication of microring structures containing gold nanoparticles and shows their potential to exploit them for surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) based applications.
Source: [10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.143752]

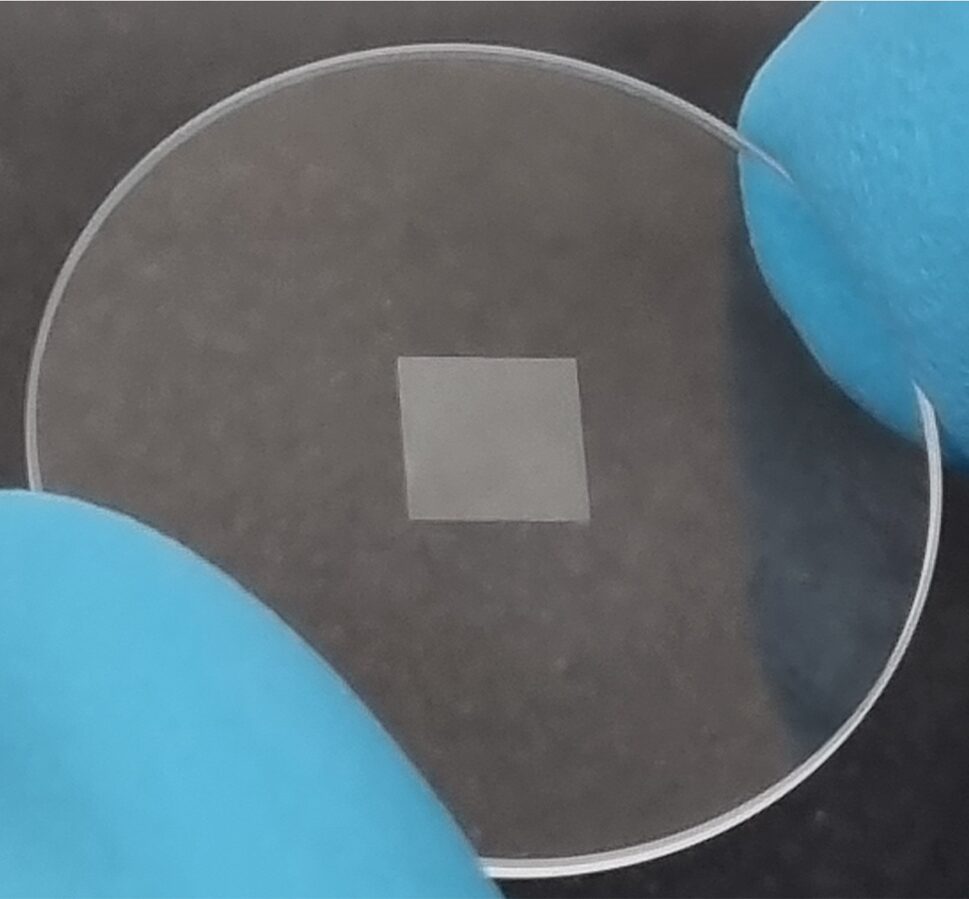
FABRICATION OF SERS SUBSTRATES USING GOLD FILMS TREATMENT
The suggested fabrication approach of the SERS substrate is simple, reliable, and cost-effective compared to lithographical methods. The main advantages of the nanosecond laser treatment are the short processing time, simple sample preparation process, submicron treatment accuracy, repeatability of samples, the low thermal impact to the substrate and surrounding areas, and the selective generation of nanoparticles at the desired place and of the desired shape at the surface. The estimated enhancement factor of the fabricated SERS substrates is 106, similar to the conventional SERS enhancement factor.
Source: [10.1021/acsomega.1c05165]
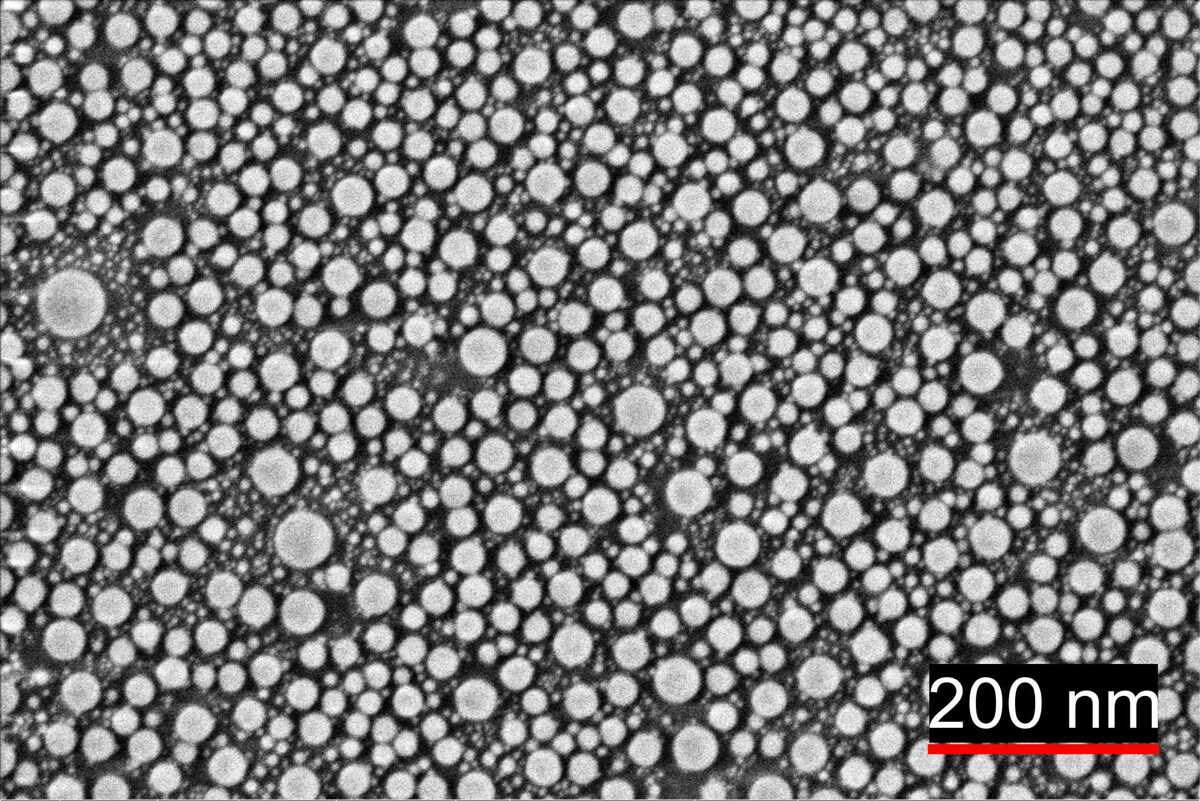
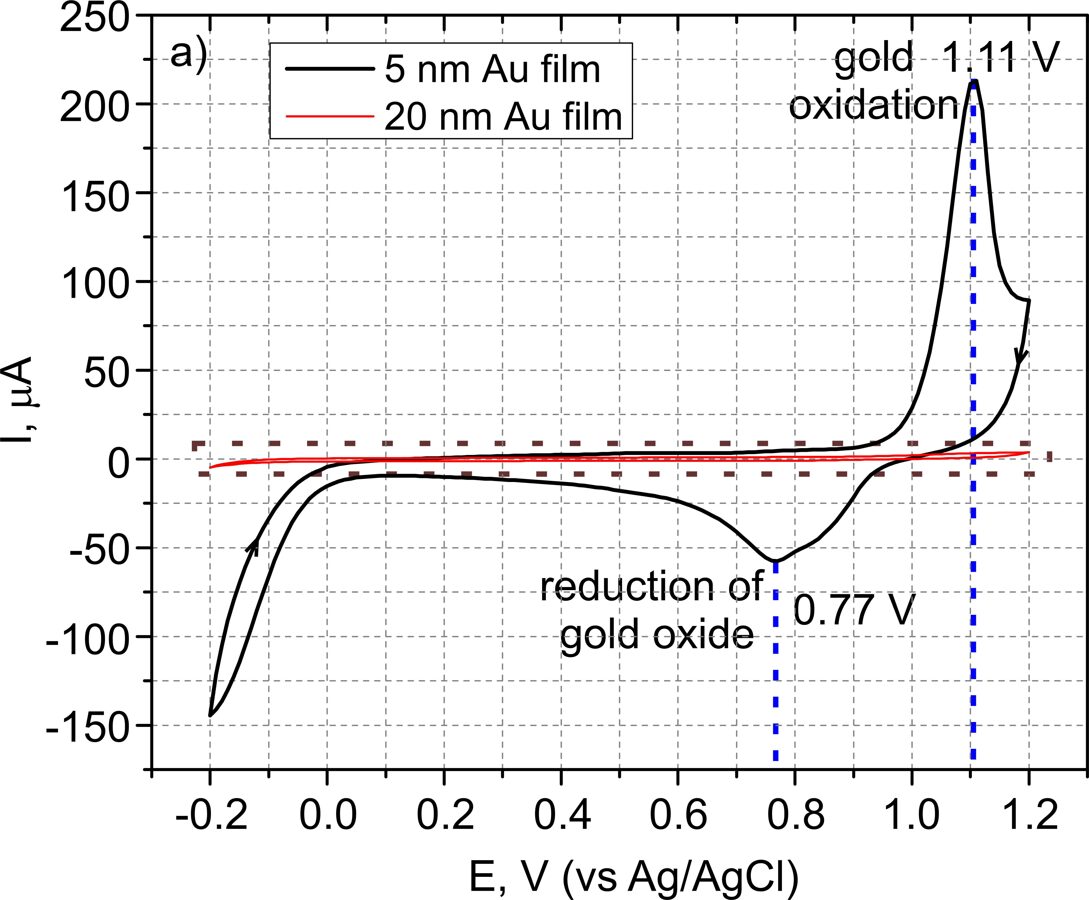
LASER GENERATED NANOPARTICLES USED IN ELECTROCHEMISTRY
The problem of attachment of gold nanoparticles was solved by a one-step generation of gold nanoparticles directly on the ITO glass by using nanosecond laser pulses. Detailed electrochemical characterization of these nanoparticles was performed using cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. For the first time, a potential application of these gold nanoparticles was tested for response to ascorbate as a possible use for electrochemical sensing.
Source: [10.1016/j.electacta.2018.11.197]
CONTACT FORM
You can contact us by filling out this form